Ever wondered what it takes to become a beekeeper? You’re in the right place! This guide simplifies the journey so anyone — even complete beginners — can start confidently. Beekeeping is more than a hobby; it’s a way of caring for nature’s most essential insects and enjoying the sweet rewards they bring.
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand how to set up a beehive, manage colonies, harvest honey, and connect with fellow bee enthusiasts. Let’s begin this exciting adventure — where you’ll support pollinators, nurture healthy hives, and savor the golden nectar they produce.
Understanding Beekeeping
Becoming a successful beekeeper starts with a foundation of knowledge. Before you bring bees home, take time to understand their biology, behavior, and habitat.
Research and Education
Books, Online Resources, and Courses:
Start by immersing yourself in books and online materials dedicated to beekeeping. From hive management to seasonal care, these resources offer practical insights. Online courses or workshops are especially helpful for learning hands-on techniques.
Join Local Beekeeping Associations:
Connecting with your local beekeeping community is invaluable. Local associations or clubs let you exchange ideas, seek mentorship, and gain experience from seasoned keepers. They can also guide you on region-specific bee behavior and hive management.

Basic Knowledge of Bee Biology and Behavior
Types of Bees in a Hive:
Every hive functions through teamwork — the queen, worker bees, and drones. The queen lays eggs, workers maintain the hive and gather nectar, while drones focus on mating. Knowing these roles is key to managing colony health.
Life Cycle of Bees:
Understanding the stages from egg to adult bee helps you predict the needs of your hive throughout the year.
Essential Beekeeping Equipment
Before you begin, invest in reliable protective gear and tools. High-quality gear ensures comfort and safety, especially when inspecting hives or harvesting honey.
-
Beekeeping Jackets: A good jacket offers breathable protection and prevents stings while keeping you cool during inspections.
-
Beekeeping Gloves: Durable gloves provide flexibility and safety when handling frames or bees.
-
Beekeeping Veils: Protect your face and neck from bee stings while maintaining clear visibility.
-
Beekeeping Trousers: Lightweight trousers prevent stings through clothing and enhance mobility.
-
Beekeeping Suits: A full suit offers head-to-toe protection, perfect for beginners and professionals alike.
-
Beekeeping Kids Suits: For families who beekeep together, children’s suits make learning fun and safe.
-
Beekeeping Ankle Protection: Keeps ankles sting-free — especially useful in warmer months when bees are most active.
Brands like Oz Armour are widely trusted among professionals for their ventilated, comfortable, and sting-resistant gear. Their range balances safety, breathability, and comfort — all crucial for enjoyable beekeeping sessions.
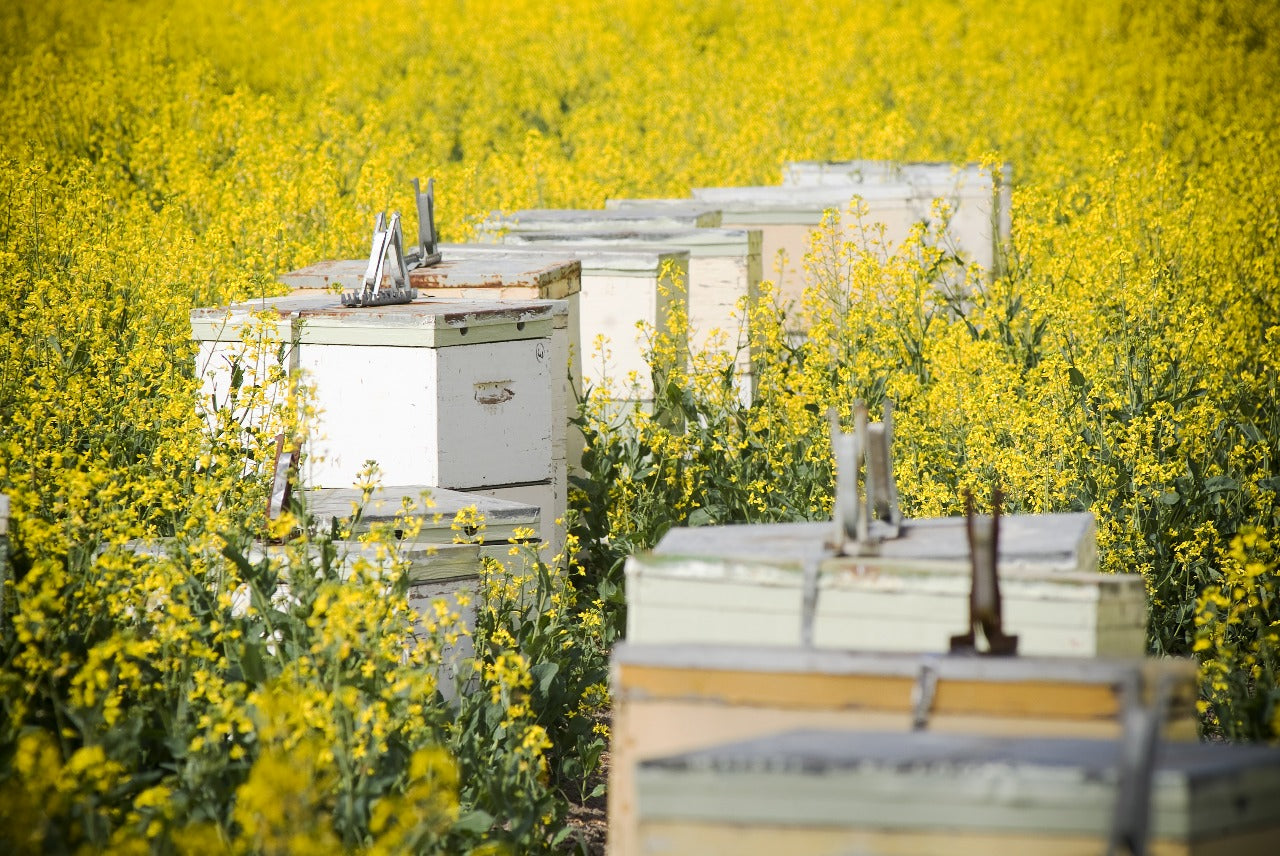
Setting Up Your Beehive
Setting up your hive correctly is the foundation of your success.
Location
Choose a sunny, calm location sheltered from wind, facing south or southeast if possible. Make sure bees have nearby access to water. Check your local regulations for any permit requirements regarding hive placement.
Choosing the Right Hive Type
There are three common hive types: Langstroth, Top Bar, and Warre hives.
-
Langstroth hives are most popular for beginners — easy to inspect and ideal for honey production.
-
Top Bar hives are low-maintenance and more natural but yield less honey.
-
Warre hives mimic bees’ natural nesting behavior and require less interference.
Research which style fits your goals and comfort level before investing.
Assembling and Preparing the Hive
Whether you buy a pre-made hive or build one yourself, ensure it’s assembled tightly with no gaps. Paint the exterior with light colors to regulate temperature and prevent wood decay.
Acquiring Bees
There are several ways to start your first colony:
-
Nucleus Colonies (Nucs): Miniature, established colonies with a queen, brood, and workers. Ideal for beginners.
-
Package Bees: Contain worker bees and a mated queen, shipped in a ventilated box.
-
Catching a Swarm: A cost-free but advanced method requiring experience and safety precautions.
Once your bees arrive, gently introduce them to their new hive and monitor closely for the first few weeks.
Hive Management
Proper hive management ensures colony health and productivity.
Regular Inspections
Inspect hives every 7–10 days during active months. Look for:
-
A healthy queen and brood pattern
-
Sufficient honey and pollen stores
-
Signs of pests or disease
Feeding Bees
Feed sugar syrup (2:1 ratio) in spring and pollen substitutes during nectar shortages. This helps colonies build strength before major honey flows.
Pest and Disease Control
Keep an eye out for Varroa mites, small hive beetles, and foulbrood. Treatments include organic options like powdered sugar dusting or essential oils and, when necessary, chemical controls under proper guidance.
Harvesting Honey
The most rewarding part of beekeeping is collecting honey — but timing matters. Harvest only when most frames are capped with wax, signaling ripeness.
Extraction Process
-
Smoke the hive gently to calm the bees.
-
Remove capped honey frames.
-
Uncap using a heated knife or fork.
-
Spin in a honey extractor and collect the liquid gold.
After extraction, let the honey settle to remove bubbles and impurities. Store in clean, airtight jars in a cool, dark place. Proper storage maintains flavor, aroma, and texture.
Beeswax and Other Bee Products
Beekeeping isn’t just about honey — bees produce wax, pollen, propolis, and royal jelly.
-
Beeswax: Melt and strain wax cappings for candles, balms, and crafts.
-
Propolis: A resin collected from trees, used for natural remedies and hive protection.
-
Royal Jelly: A nutrient-rich substance known for potential health benefits.
-
Pollen: A protein powerhouse harvested from traps at hive entrances.
Harvesting these products adds diversity and sustainability to your beekeeping operation.
Safety and Comfort: The Importance of Proper Gear
Beekeeping safety shouldn’t be overlooked. Reliable protective wear — such as beekeeping jackets, gloves, and veils — not only prevents stings but also builds confidence while handling hives.
Beekeepers worldwide value Oz Armour’s gear for its three-layer ventilated mesh suits, designed to offer maximum sting protection while allowing airflow in warm climates. The brand’s thoughtful craftsmanship has made it a top choice among both hobbyists and professionals.
Joining the Beekeeping Community
Beekeeping becomes even more enjoyable when shared with others. Join online forums, attend local workshops, or collaborate on honey harvests. Sharing experiences helps refine your techniques and stay updated on regional trends or issues.

Final Thoughts
Beekeeping is more than just tending to bees — it’s a rewarding connection to nature and a commitment to sustainability. From setting up your first hive to harvesting honey and creating beeswax products, every step brings a sense of accomplishment and wonder.
Whether you’re learning about bee biology, investing in high-quality beekeeping suits, or exploring ankle protection gear, preparation and patience will help your colonies thrive.
For families, encouraging young ones with kids’ beekeeping suits can spark a lifelong appreciation for pollinators and sustainability.
In the end, beekeeping isn’t just about producing honey — it’s about contributing to ecological balance, supporting pollination, and enjoying the bond between humans and bees. With trusted gear from Oz Armour and continuous learning, your journey into beekeeping will be both safe and fulfilling.
👉 Continue your learning journey and read more blogs about beekeeping.